Unveiling the Distinctions: Data Analytics vs. Data Analysis
In the evolving landscape of data-driven decision-making, terms like “Data Analytics” and “Data Analysis” are often used interchangeably. However, a closer examination reveals distinct roles and methodologies within these umbrella terms. Let’s unravel the intricacies and understand the unique contributions of each in the realm of harnessing insights from data.
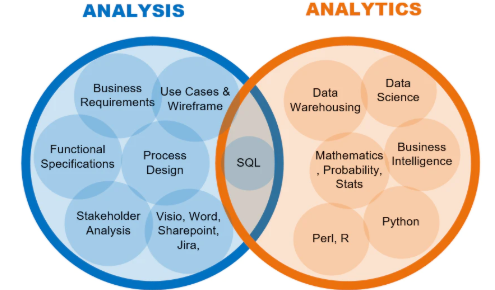
Understanding Data Analysis: The Foundation
At its core, data analysis involves inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover meaningful information, reach conclusions, and support decision-making. It encompasses a wide array of techniques, from basic statistical measures to complex algorithms, with the primary goal of extracting actionable insights. Data analysis often involves examining historical data to identify trends, patterns, and outliers.
Key Characteristics of Data Analysis:
- Historical Focus: Primarily retrospective, analyzing past data to gain insights into what has occurred.
- Structured Approach: Involves a systematic examination of data to draw conclusions and make informed decisions.
- Statistical Techniques: Utilizes statistical methods to interpret data and draw meaningful inferences.
Transitioning to Data Analytics: Beyond the Basics
Data analytics extends the scope of data analysis by incorporating advanced techniques and tools to uncover deeper insights, trends, and predictive patterns. It involves the integration of statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling to guide decision-making processes. Data analytics is forward-looking, aiming to anticipate future trends and behaviors based on historical data.
Key Characteristics of Data Analytics:
- Predictive Focus: Utilizes forecasting and predictive modeling to anticipate future trends and behaviors.
- Advanced Techniques: Incorporates machine learning algorithms and statistical models for complex analysis.
- Decision Support: Offers insights that inform strategic decision-making and business planning.
Navigating the Differences:
- Scope and Objectives:
- Data Analysis: Focuses on examining historical data to draw conclusions and inform decisions.
- Data Analytics: Encompasses a broader scope, incorporating predictive modeling and advanced techniques to guide future decision-making.
- Techniques and Tools:
- Data Analysis: Involves basic statistical measures and structured methods.
- Data Analytics: Integrates advanced tools like machine learning algorithms for complex analysis.
- Application:
- Data Analysis: Primarily retrospective, addressing current business challenges based on historical data.
- Data Analytics: Prospective, aiming to provide insights that support long-term strategic planning.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Both data analysis and data analytics play pivotal roles in extracting valuable insights from data. The choice between the two depends on the specific objectives, timeframe, and complexity of the analysis required. While data analysis serves as the foundation, data analytics propels organizations into a future-oriented approach, equipping them to make informed decisions in an increasingly data-driven world. By understanding the nuances of each, businesses can leverage the right approach to extract maximum value from their data assets.
Author
